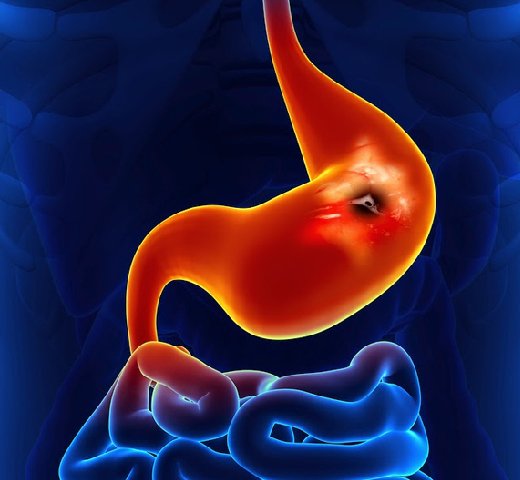
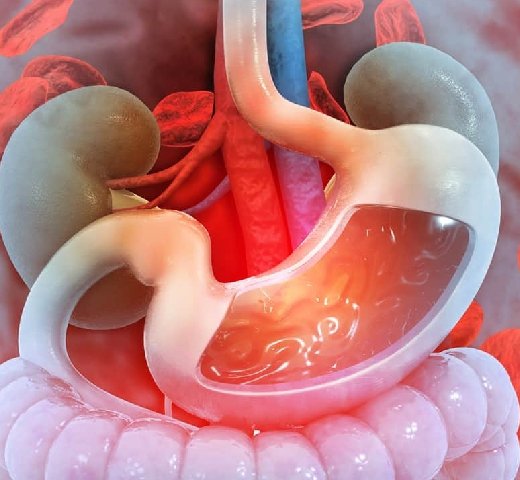
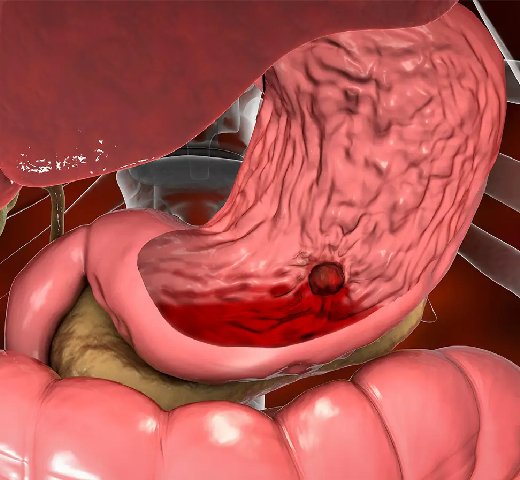
G.I. bleeding, or gastrointestinal bleeding, refers to any form of bleeding that occurs in the gastrointestinal tract, which spans from the mouth to the anus. It is categorized into upper G.I. bleeding (from the esophagus, stomach, or upper small intestine) and lower G.I. bleeding (from the lower small intestine, colon, rectum, or anus).
G.I. BLEEDING TREATMENT
G.I. (Gastrointestinal) bleeding treatment encompasses a range of medical interventions aimed at stopping bleeding within the gastrointestinal tract, which includes the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine (colon), rectum, and anus. The approach to treatment depends on the source, severity, and cause of the bleeding. Initial steps often involve stabilizing the patient, possibly through IV fluids or blood transfusions. Diagnostic procedures like endoscopy may be used to locate the bleed and allow for direct treatments such as cauterization, clipping of bleeding vessels, or injection of substances to promote clotting. In severe cases, surgery may be required to repair the bleeding site. Treatment also includes addressing underlying conditions that caused the bleeding, such as ulcers, diverticulosis, or inflammatory bowel disease, to prevent recurrence.
Dr. Sanjay K. Agrawal, a preeminent Consultant Gastroenterologist in Raipur, offers comprehensive treatment for G.I. bleeding with a focus on precision, patient safety, and efficacy. Leveraging his extensive expertise, Dr. Agrawal utilizes advanced diagnostic and therapeutic techniques to identify the source of gastrointestinal bleeding swiftly. His approach typically involves endoscopy, which allows for direct visualization and immediate treatment of bleeding sites through methods such as cauterization, clipping, or the administration of therapeutic agents. Emphasizing a holistic care model, Dr. Agrawal also addresses underlying conditions to prevent future episodes, ensuring personalized patient management. His dedication to employing the latest in gastroenterological practices assures optimal outcomes and improved quality of life for patients facing G.I. bleeding issues.
Here Are
G.I. BLEEDING TREATMENT F&Q's
Signs of G.I. bleeding can vary and may include vomiting blood, black or tarry stools, bright red blood in stools, or stools that appear dark and sticky. Symptoms also might include dizziness, weakness, and a decrease in blood pressure, indicating significant blood loss.
Causes of G.I. bleeding include peptic ulcers, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), erosive esophagitis, diverticulosis, colorectal cancer, hemorrhoids, and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), among others.
Diagnosis typically involves endoscopic procedures like a gastroscopy for upper G.I. bleeding or a colonoscopy for lower G.I. bleeding. Additional tests may include blood tests, stool tests, and imaging studies like a CT scan to identify the bleeding source and assess its severity.
Treatment depends on the bleeding's cause and location but may include endoscopic techniques to directly stop the bleeding, such as thermal coagulation, clipping, or banding. Medications to reduce stomach acid and treat underlying conditions might be used. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary.
While not all cases can be prevented, risk reduction measures include limiting NSAID pain relievers, managing chronic conditions like GERD, and following recommendations for the screening and treatment of conditions like peptic ulcers and colorectal cancer. Lifestyle changes, such as moderating alcohol intake and quitting smoking, can also help reduce risks.